Architectures for Modern Web Applications
Modular tech stacks enable teams to work flexibly and quickly adapt to changes in scope.
OverviewAnchor
Modern web applications have become a pillar of the modern web experience. With an API-first modular architecture, teams are able to work efficiently, find a balance between the cutting edge and the tried-and-true technologies to provide fast, user-focused experiences in a web application.
Whether teams are launching a new project and want to get up and running quickly, or wish to update an existing stack, teams are able to build modern web applications without having to reinvent the wheel when working with a modular, API-first tech stack. Modular tech stacks enable teams to work flexibly and quickly adapt to changes in scope without having to consider each system’s maintenance, scalability, or vendor lock-in.
As teams begin to search for tools to build their modular, API-first tech stack, it can be a daunting task. That’s why we have created some high-level architectures to give you a place to start and serve as a guide for building an optimized modular tech stack.
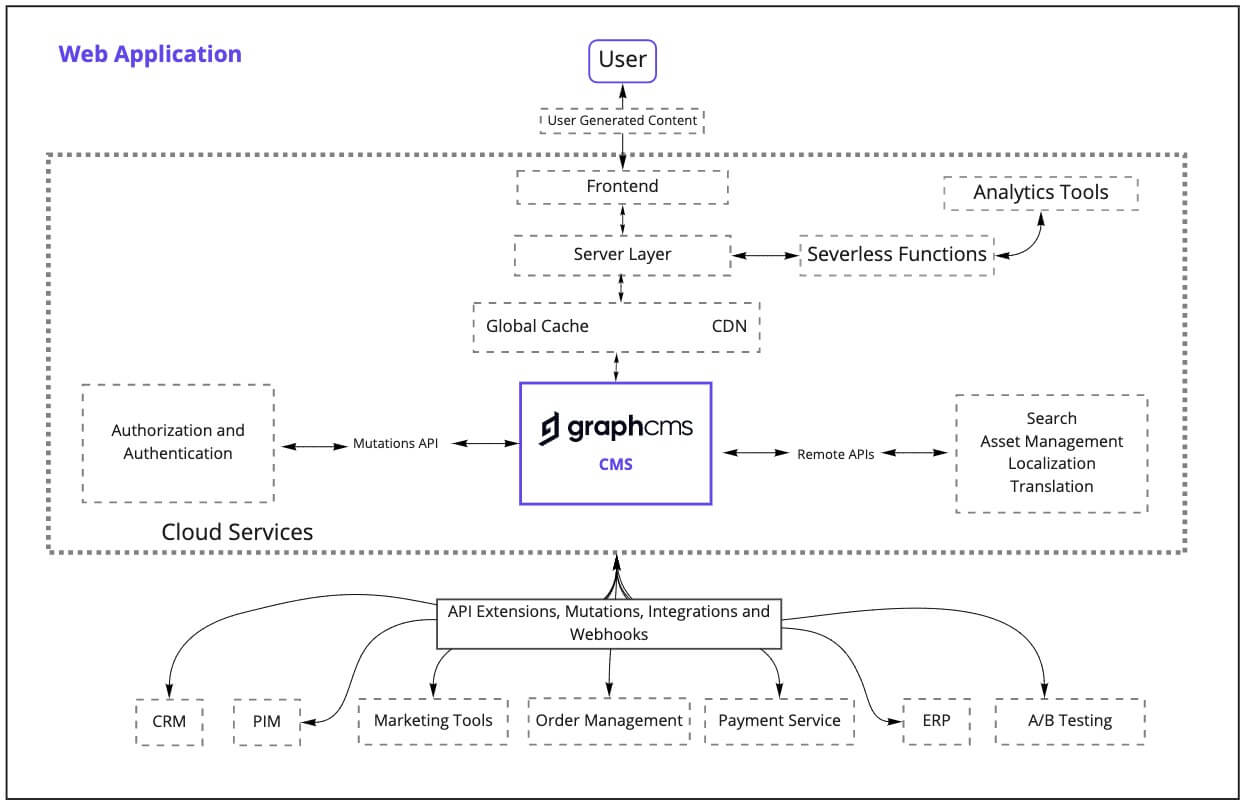
ArchitectureAnchor
To view the high-resolution version of this architecture, you can view the higher resolution version here.
Architecture BreakdownAnchor
Authentication/AuthorizationAnchor
Authentication and Authorization software center around confirming the identity of users and ensuring that only the correct people have access to the system. Systems such as Okta and Onelogin are popular choices for handling authentication and authorization.
Global CacheAnchor
Global caching improves performance by storing copies of files or data in regions that are globally distributed. Future requests of the same data are pulled from the region closest to the request enabling the data to load more quickly. This can be particularly helpful for content that is accessed repeatedly. Cloudflare is a popular option due to its robust network of data centers.
CDNAnchor
A content delivery network (CDN) is a globally distributed group of servers that allow for quick transfer of assets. CDNs reduce hosting bandwidth and can improve security by pulling content closer to website visitors.
AnalyticsAnchor
Analytics is a broad category of tools that are critical for having oversight on the performance of a website. These tools can be essential for ensuring the health of a website and can give an overview of the status of various pages and services. Popular tools such as Google Analytics give users insights into page speed, traffic, errors, and more. Analytics tools can be useful for planning based on concrete information such as user engagement.
Asset ManagementAnchor
Asset Management tools make it easy to upload, transform, manipulate assets for your website or digital project. These services give users more control over their assets, a critical component of any modern digital project. Popular tools for asset management include Filestack and Fastly.
PersonalizationAnchor
Personalization tools allow teams to test and iterate content, easily. They make it easy for teams to understand how different content (such as wording, case studies, assets, or even user journeys) performs relative to one another. These tools serve multiple variations of content and collect data on the performance. Tools such as Optimizely and Dynamic Yield are popular options for A/B Testing and Personalization.
Localization and TranslationAnchor
Localization and translation services help digital products serve the needs of a globalized user base. These tools range in their specific product offering; however, they either allow for easy translation or localization of content. This can be particularly helpful if localization is being outsourced or are looking to use an AI translation tool.
API-first ServicesAnchor
API-first services is a general way to describe how easy it is to connect using case-specific services that have an API. With GraphCMS these services can be connected in a variety of ways, including via content federation or using the Mutations API. API-first services make it easy for teams to create their ideal tech stacks without having to build them themselves from scratch.
CRMAnchor
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tool is a tool that is used to better oversee interactions with users and to streamline relationship building. CRMs store and organize contacts, user interactions, and deal progression for sales teams. Tools such as Salesforce, Hubspot, and Pipedrive are popular depending on teams’ needs.
ERPAnchor
An ERP is a software that helps companies manage business processes. These processes can range from accounting to human resources, to order processing depending on the service and needs. As these services are often integrated the look and feel across various services tends to be similar. Oracle and SAP are some of the wider-known ERP vendors.
PaymentsAnchor
Payment Service Providers allow online shops to accept online payments. These payments can come in the form of credit card payments, bank transfers, or third-party services, such as Paypal, depending on the configuration of the service. One example of a popular payment service provider is Stripe.
Order ManagementAnchor
Order Management systems track sales, orders, inventory, and fulfillment to make digital commerce more streamlined and efficient. OMS solutions house a wide range of information including product information and order tracking.
PIMAnchor
A PIM serves as a single source to manage and enrich product information which can then be distributed to sales and commerce channels. PIMs ensure that data around a product is current and can easily be distributed where necessary throughout the buying experience. Popular PIMs include akeneo and PIMcore.
User Generated ContentAnchor
User-Generated Content (UGC) is any content that is created by people rather than companies or branding companies. UGC could be anything from reviews, content, or assets created by users - or a combination of interactions, preferences, and attributes depending on a user's behavior within an app.
Architecture Best PracticesAnchor
In order to get the most out of your modular, API-first tech stack for a modern web application, there are some critical best practices that should be considered.
Invest time at the beginning of the projectAnchor
With modular architectures, it is critical that data flows freely from one service to another in order to maintain a high-quality user experience. Ensuring that services can easily communicate with one another to avoid content silos should be a careful consideration during the planning process. While it may be a good idea for data to have a single home where it can be manipulated, it should still be distributed to the necessary systems to keep architectures tidy and data current.
Ensure the redundancies are intentionalAnchor
While it may be the case that you want to build some redundancies into your tech stack for extra security, it is important to make sure that they serve a real purpose. Creating too many redundancies or unnecessary ones can lead to a bloated tech stack rather than an agile, flexible system.
Decentralize the various componentsAnchor
Part of breaking down the monolith is enabling best-of-breed services to specialize. This approach ensures that teams have all of the functionality they need without being weighed down by unnecessary dead weight. Decentralizing systems may take some refinement over time but it is certainly worth the time investment. When systems are communicating via API, it becomes much easier to add and remove services without disrupting existing data.
Consider data privacy standards when choosing servicesAnchor
Data privacy varies wildly from region to region and it is important to consider how various services will handle data. For example, the EU has much stricter data privacy laws than other countries. Ensuring that data is stored in the regions that match your standards can be a key consideration when choosing your tech stack.